Industry-specific attributes
|
Structure |
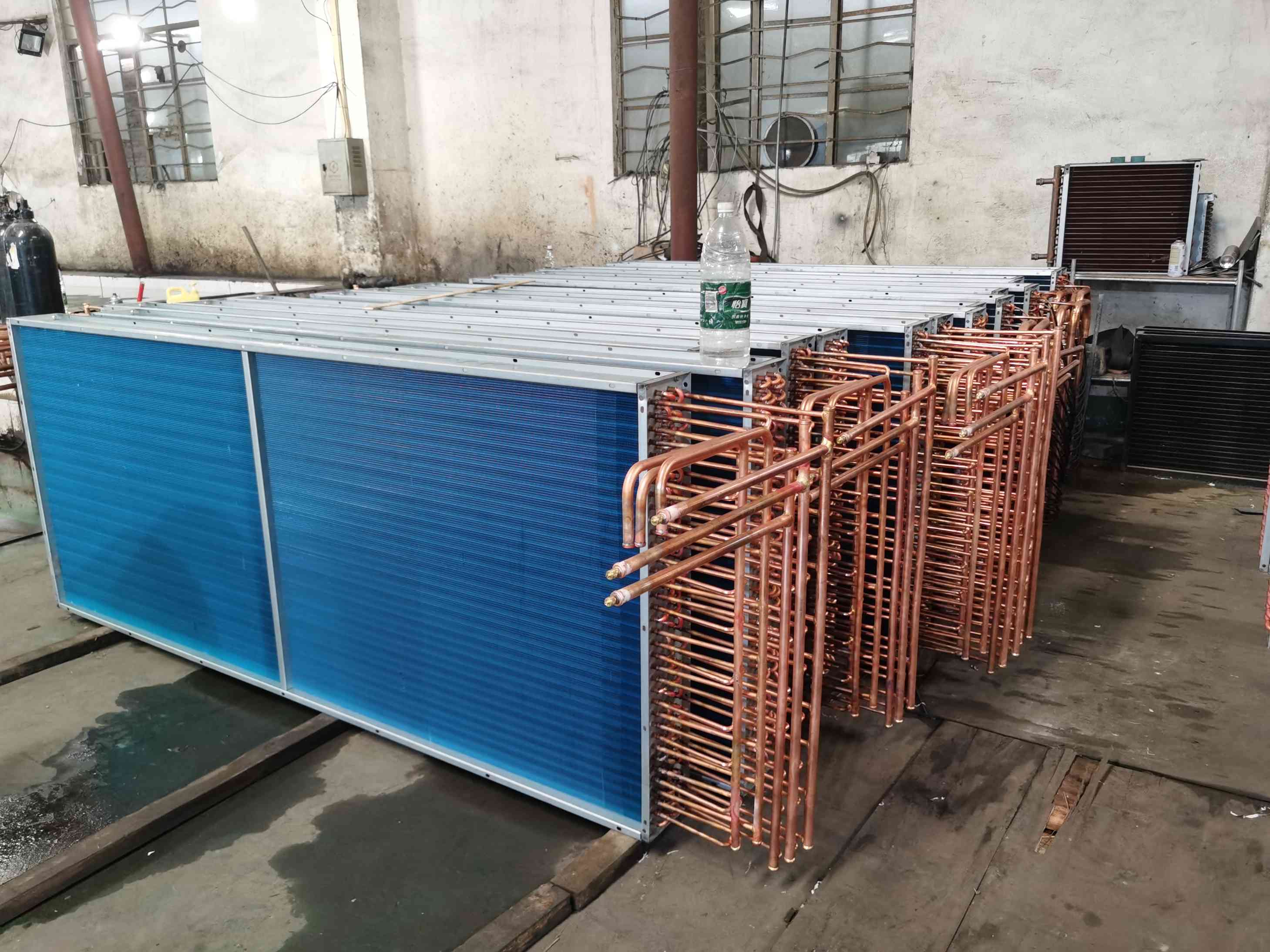
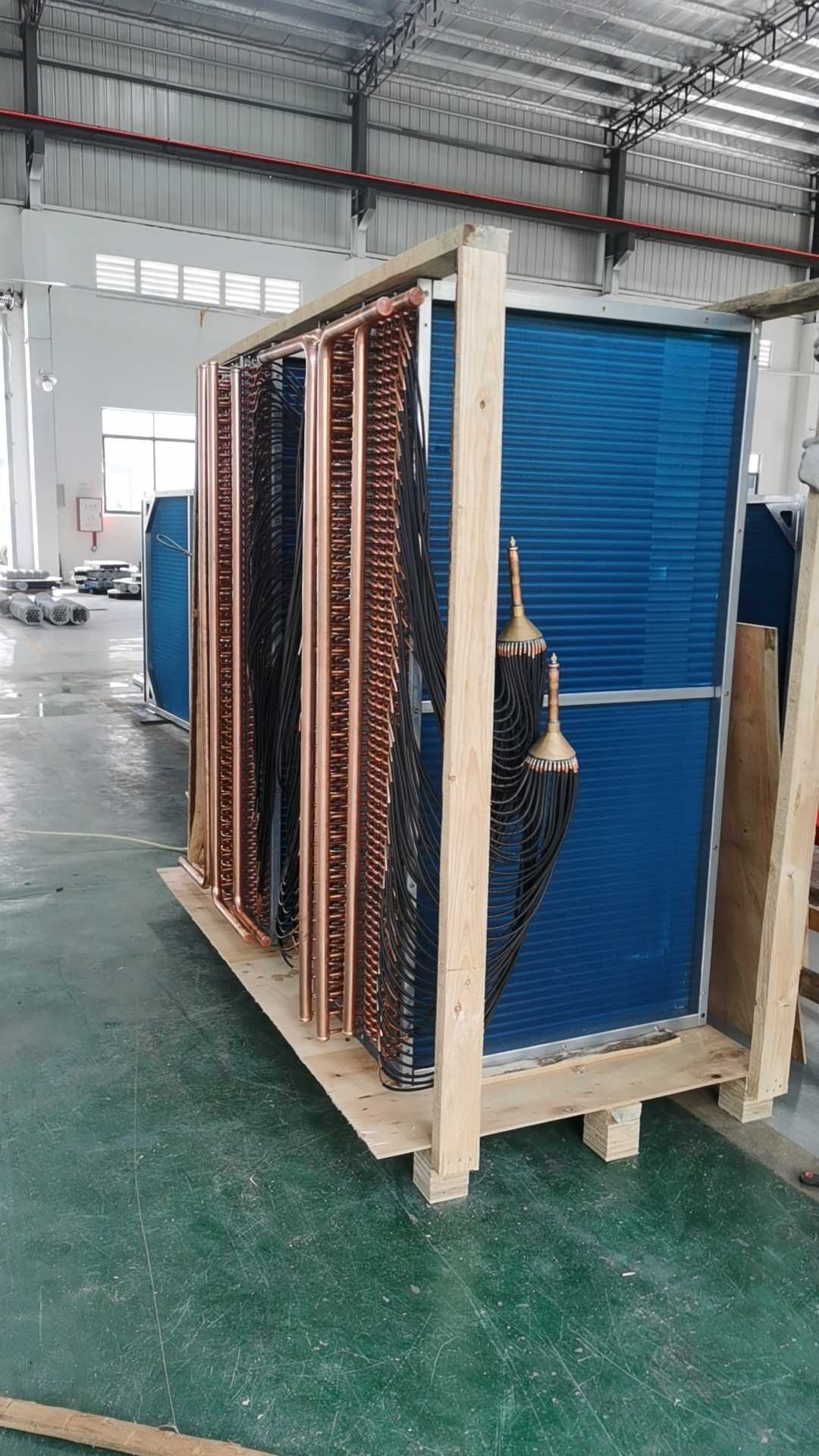
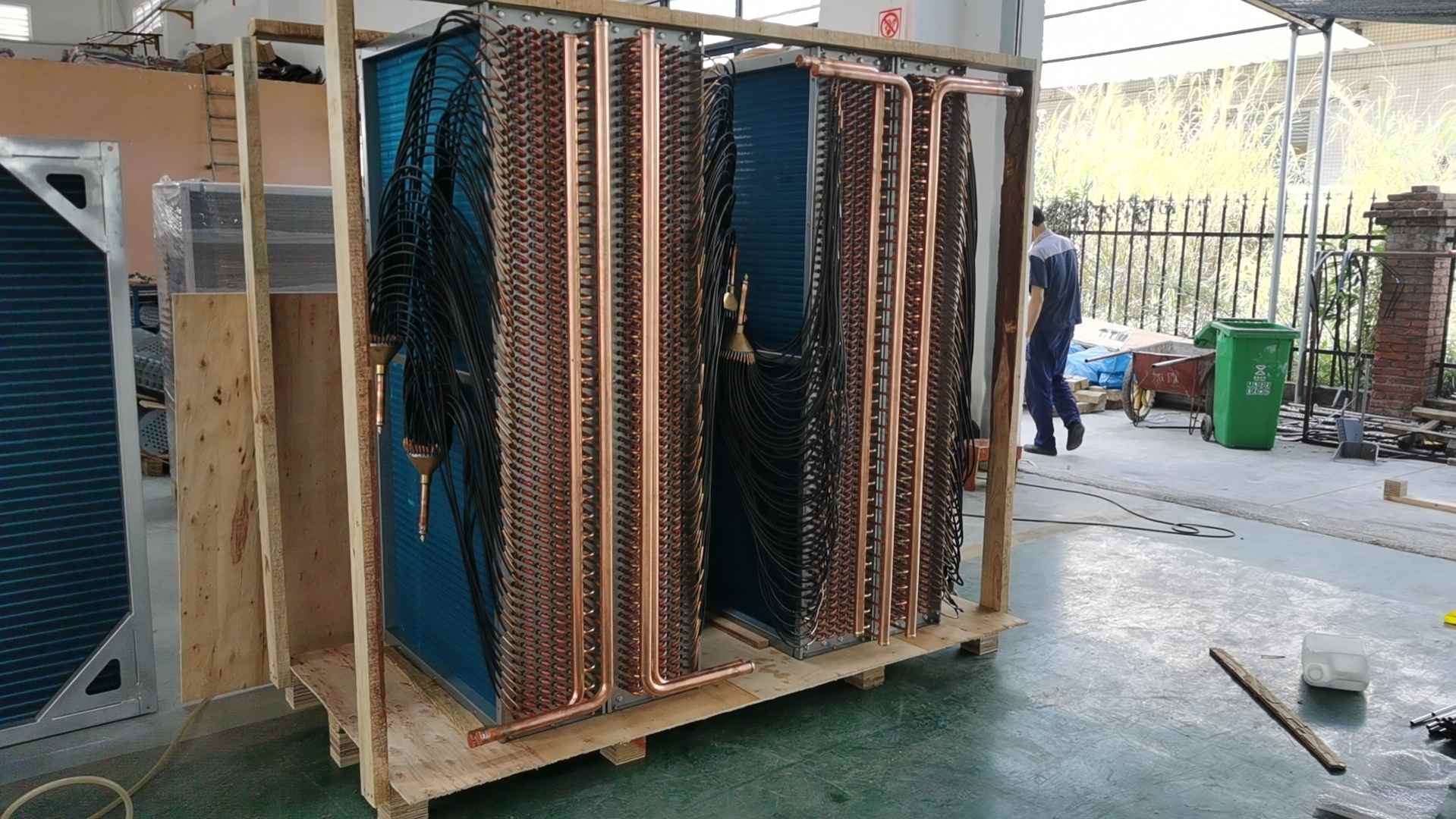
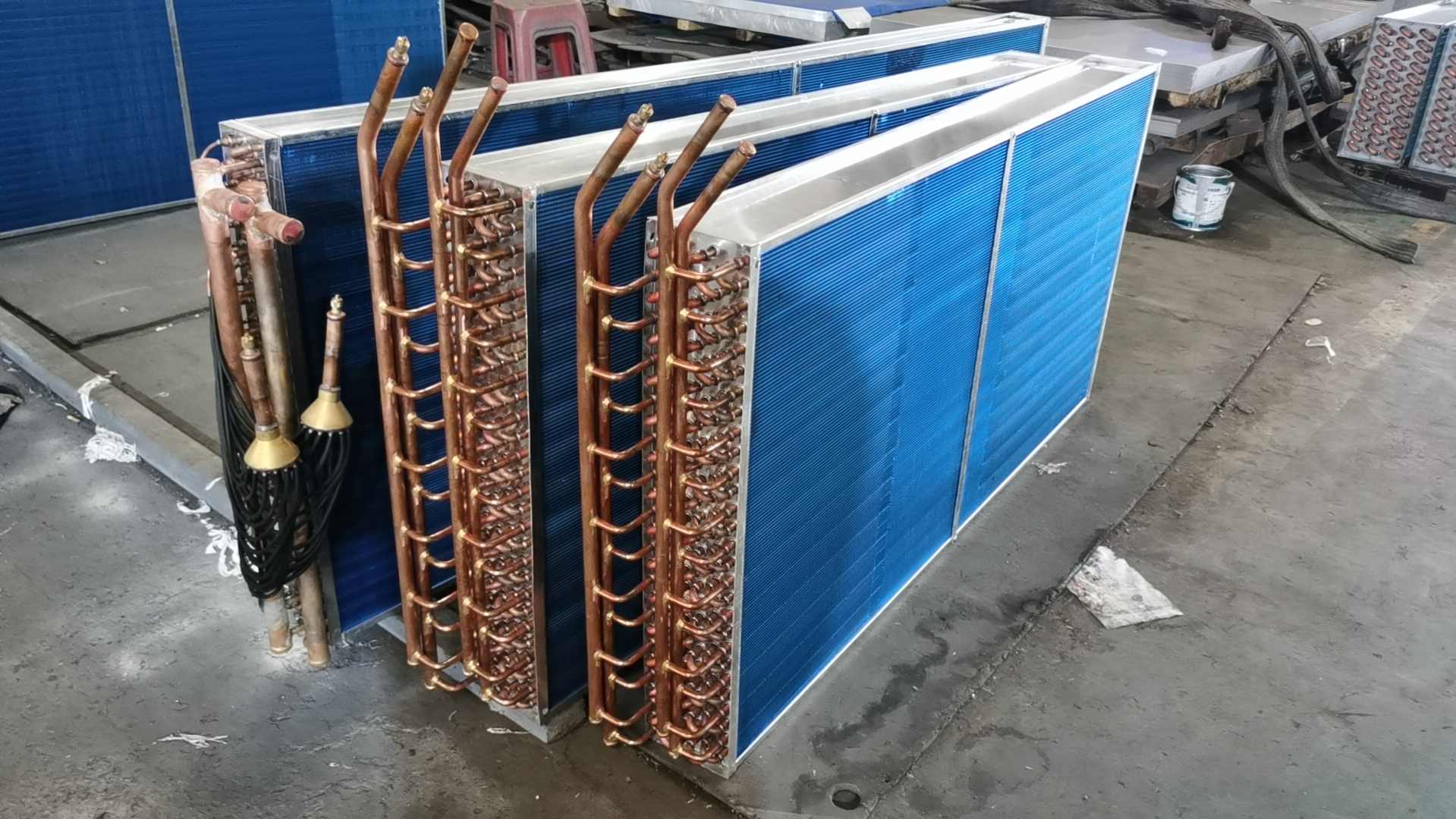
condenser coil |
|
Voltage |
220V/380V |
Finned heat exchanger, factory mold specifications
|
Diameter |
Fin spacing |
Hole spacing |
Row spacing |
|
9.52mm |
1.80-6.00mm |
25.00mm |
21.65mm |
|
12.70mm |
1.80-6.50mm |
31.75mm |
27.50mm |
|
15.88mm |
1.80-9.00mm |
38.10mm |
33.00mm |
Other attributes
|
Applicable Industries |
hotels, Garment Shops, Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms, Restaurant, Home Use, Retail, Construction works , Energy & Mining, Food & Beverage Shops |
|
Showroom Location |
Foshan China |
|
Video outgoing-inspection |
Provided |
|
Machinery Test Report |
Provided |
|
Warranty of core components |
1 Year |
|
Core Components |
PLC |
|
Place of Origin |
Guangdong, China |
|
Weight |
10 KG |
|
Warranty |
1 Year |
|
Key Selling Points |
leakproof |
|
Condition |
New |
|
Brand Name |
EVER HEAT |
|
Liquid Flow Rate |
2.5m/s |
|
Maximum Working Pressure |
Variable |
|
Dimension(L*W*H) |
Request |
|
Working Temperature Range |
Customize on request |
|
After-sales Service Provided: |
Engineers available to service machinery overseas |
|
Feature |
High energy efficiency-low operating cost, |
|
Type |
Finned tube condenser coil |
|
Material |
All Kind of Material can be applied |
|
Application |
refrigeration condenser |
|
Certification |
TUV, CE |
|
Heat exchanger type |
refrigeration condenser |
|
Whether to accept small orders |
Yes |
|
Function |
Refrigeration Heat Exchange Equipment |